D-Alanine Metabolism
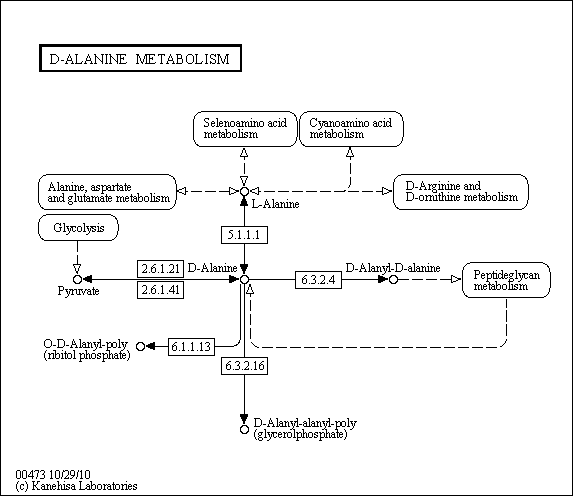
Description: The naturally occurring L-Alanine isomer is racemized to its D-form through the action of a class of enzymes called AlRs. These enzymes are ubiquitous among prokaryotes, and with very few exceptions, are absent in eukaryotes, making them a logical target for the development of novel antibiotics. AlR catalyzes the racemization of L-Alanine and D-Alanine, using Pyridoxal 5'-Phosphate (Vitamin-B6) as a cofactor, which is the first step in D-Alanine metabolism. L-Alanine can also be formed from Pyruvic acid, obtained from the process of Glycolysis and by the action of enzyme D-Methionine Transaminase and D-Alanine Transaminase that reconverts to Pyruvate (Ref.5). L-Alanine is also a product of several other metabolic pathways like Cyanoamino Acid Metabolism, Selenoamino Acid Metabolism, Alanine and Aspartate, and D-Arginine and D-Ornithine Metabolism. D-Alanine Transaminase catalyzes the formation of Pyruvic acid during D-Alanine metabolism by using D-Alanine and 2-Oxoglutarate as its substrates to carry out the reaction. The enzyme helps in transferring the amino group from D-Alanine to Oxoglutaric acid, which is then converted to Glutamic acid, and finally to Pyruvic acid. Another enzyme D-Alanyl-Poly (Phosphoglycerol) Synthetase catalyzes the formation of D-Alanyl-Alanyl-Poly (Glycerolphosphate) during D-Alanine metabolism. It uses D-Alanine and Alanyl-Poly (Glycerolphosphate) as its substrates to produce D-Alanyl-Alanyl-Poly (Glycerolphosphate). During the reaction, the enzyme uses the energy of an ATP to transiently form the bond between D-Alanine and Alanyl-Poly (Glycerolphosphate) to form the product along with the release of ADP and a phosphate group as byproducts of the reaction. In the next step, DDLB catalyzes the synthesis of D-Alanyl-D-Alanine by forming a bond between the hydroxyl group of one D-Alanine molecule and the amino group of the other molecule. The formation of this bond releases a water molecule and leads to the formation of D-Alanyl-D-Alanine. The enzyme utilizes the energy of an ATP to carry out the reaction and cleaves it to produce an ADP along with an orthophosphate group. DltA (D-Alanine-Poly(Phosphoribitol) Ligase) catalyzes the formation of O-D-Alanyl-Poly(Ribitol Phosphate) by forming a thioester bond between D-Alanine and the sulfhydryl group of the 4'-Phosphopantetheine prosthetic group of D-Alanine carrier protein, Poly (Ribitol Phosphate), which activates the alanine and finally produces O-D-Alanyl-Poly (Ribitol Phosphate). The enzyme uses the energy of an ATP to transiently form the thioester bond between D-Alanine and Poly (Ribitol Phosphate) to form the product along with the release of AMP and diphosphate as byproducts of the reaction. Source: Protein Lounge
Related BMRB Molecules
For complete information about pathway, see KEGG [map00473]
